- DPF traps soot and requires regeneration during operation.
- Passive regen occurs automatically on long drives; active regen needs high temp and 60-70 km/h.
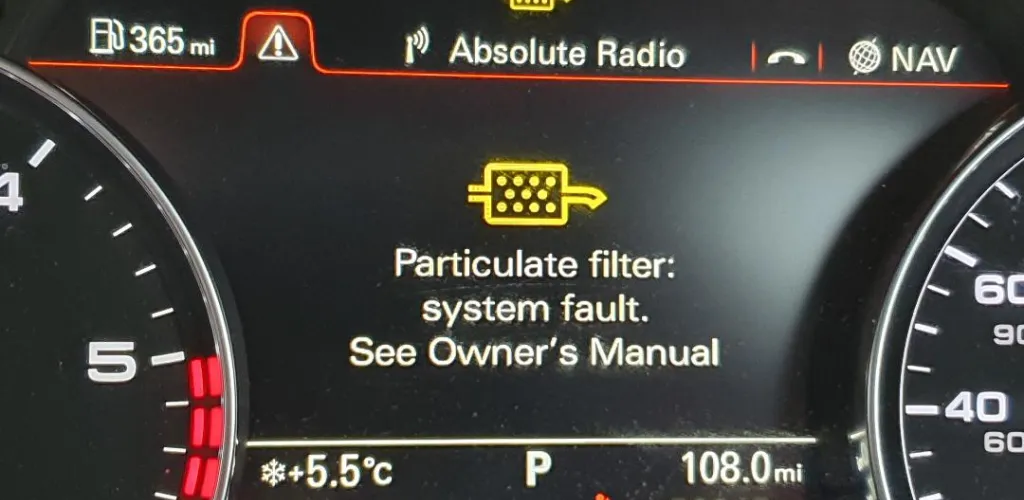
- Warning lights when soot nears critical level, clog, or sensor/fuel faults; urban driving prone.
- Yellow light: plan a 30-45 minute highway drive at 70-80 km/h, minimize stops.
Diesel engines are equipped with complex emissions control systems, and one of the most important components is the diesel particulate filter (DPF). The DPF warning light on the dashboard is a common issue faced by many diesel vehicle owners, especially those who drive predominantly in urban environments.
What is the Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF)
The diesel particulate filter is a specialized aftertreatment device that captures particles produced during the internal combustion process. These particles, which manifest as soot or ash, would have been expelled directly into the environment through the exhaust gases before DPF technology was implemented.
Technical structure of the DPF
The internal composition of a diesel particulate filter consists of a high-strength ceramic substrate, formed in a honeycomb-like structure. This design efficiently traps particles, preventing their passage through the exhaust system. Over time, a vehicle’s DPF becomes loaded with soot, requiring regeneration or automatic cleaning.
DPF regeneration process
Passive regeneration
Passive regeneration takes place continuously during normal engine operation, without driver intervention. This process requires high exhaust gas temperatures to burn off the accumulated particles. Passive regeneration works efficiently on long trips, at steady speeds and moderately to high RPM.
Active regeneration
Active regeneration is a more aggressive form of automatic DPF cleaning, triggered when the soot load reaches a critical level. This process requires meeting specific criteria:
- The engine must reach its maximum operating temperature
- The vehicle must be driven continuously at higher speeds (over 60-70 km/h)
- The process can take up to 45 minutes
- Additional fuel is injected into the aftertreatment system to increase the temperature
Stopping the vehicle during active regeneration will interrupt the process, requiring the regeneration to start over.
Why the DPF warning light comes on
A DPF uses differential pressure switches and backpressure sensors to determine the soot load. The DPF warning light comes on for the following main reasons:
- The soot load is approaching a critical level
- Passive regeneration has failed
- The filter is partially or completely clogged
- There is a fault in the pressure sensors
- Problems with injectors or the fuel supply system
Vehicles used predominantly in urban areas for short distances are the most prone to DPF problems. This happens because the engine does not reach the necessary temperature for passive regeneration, and particles accumulate continuously in the filter.
What to do when the DPF warning light comes on
Yellow steady warning light
If the DPF light remains yellow and steady, you can continue driving, but you should act quickly:
- Plan an immediate long highway trip (minimum 30-45 minutes)
- Maintain a constant speed of at least 70-80 km/h
- Avoid frequent stops until regeneration completes
- Let the engine run at moderate revs (2000-3000 RPM)
- Do not switch off the engine until the light goes out
Red or blinking warning light
If the regeneration light starts to flash or changes color from yellow to red, you must stop the vehicle immediately and not restart it. Continuing to drive risks irreparable damage to the engine or exhaust system. In this situation, contact a specialized workshop for towing and diagnostics.
Professional cleaning of the DPF
When automated regeneration is not sufficient, a specialized intervention is necessary. Professional cleaning of the DPF involves:
Manual cleaning method
- DPF removal - A complex operation requiring lifting the vehicle and disconnecting the exhaust system
- Cleaning with specialized equipment - Using ultrasonic machines or specific chemical substances
- Testing and verification - Checking the structural integrity and filtration efficiency
- Reinstallation and system reset - Reinstalling the filter and resetting ECU parameters
Costs associated with DPF cleaning
Costs for professional cleaning of the DPF vary depending on the vehicle model and the complexity of the intervention:
- DPF cleaning: 700 - 3000 RON
- Removal/installation labor: 300 - 1000 RON
- On-site visit or tow: 200 - 500 RON
- Total estimated cost: 1200 - 4500 RON
These prices can vary significantly based on the make and model of the vehicle, with premium cars (BMW, Mercedes, Audi) having the most expensive components.
DPF lifespan
The lifespan of a DPF is influenced by several factors:
Factors affecting DPF longevity
- Driving style - Frequent short urban trips dramatically reduce lifespan
- Maintenance frequency - Regular oil and air filter changes are essential
- Fuel quality - Using higher-quality diesel extends the filter’s life
- Timely regenerations - Allowing active regeneration to complete
- Engine condition - A well-maintained engine produces fewer particulates
Estimated mileage
Under normal usage:
- Mixed use: 160,000 - 200,000 km
- Predominantly highway use: 250,000 - 350,000 km
- Predominantly urban use: 100,000 - 150,000 km
DPF replacement costs
When the DPF can no longer be regenerated or cleaned, the only solution is full replacement:
- Original DPF: 2,000 - 10,000 EUR
- Aftermarket DPF: 1,000 - 4,000 EUR
- Replacement labor: 300 - 800 EUR
- Total estimated cost: 1,300 - 10,800 EUR
Prices vary significantly by vehicle make, with premium cars (BMW, Mercedes, Audi) having the most expensive components.
Tips for maintaining DPF health
To avoid problems and costs associated with the DPF, follow these recommendations:
- Take a long trip weekly — at least 30-40 km on the highway at steady speeds
- Use high-quality engine oil — only the type recommended by the manufacturer (usually Low SAPS)
- Follow service intervals — change oil according to the manufacturer’s indications
- Fuel from trusted stations — fuel quality is essential
- Do not interrupt active regenerations — if the engine is operating abnormally, let it finish the process
- Monitor fuel consumption — a significant increase may indicate DPF issues
- Regularly check oil level — frequent regenerations can raise oil level due to fuel dilution
Warning about DPF removal
Some drivers opt to completely remove the DPF to avoid maintenance and replacement costs. This practice is illegal in Romania and carries major risks:
- Legal penalties - Fines between 1,000-3,000 RON and suspension of the registration certificate
- Inability to pass the ITU/ITP - The vehicle will not pass periodic technical inspection
- Decrease in resale value - Informed buyers will avoid vehicles without a DPF
- Environmental impact - Significantly higher emissions of fine particles
- Export issues - Inability to deregister for export within the EU
ECU software may be modified to mimic the presence and proper operation of the DPF, but this can be easily detected during periodic checks or by police inspections.
Conclusion
The diesel particulate filter is an essential component of modern diesel cars, and its proper maintenance requires understanding how it works and respecting regeneration procedures. Although maintenance and replacement costs can seem high, they are far lower than legal penalties and the technical problems that can arise from neglect or removal of the DPF.
To maximize the DPF’s lifespan and avoid major costs, the most important actions are regularly taking long trips to allow full regeneration and using only high-quality fuel and lubricants.