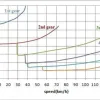
- Steady speed, road conditions, maintenance, tire pressure, driving style, and age drive fuel use.
- Six reduction tips cover fluids, tire pressure, weight, constant speed, driving style, and idling.
- Check essential fluids, tire pressure, and remove unnecessary weight to save fuel.
- Maintain constant speed and anticipate traffic to improve efficiency in cold weather.
Fuel consumption is one of the most significant operational costs for any professional driver or transport company. Understanding the factors that influence consumption and applying simple optimization measures can lead to meaningful savings, especially during the cold season when road conditions become tougher.
Below are the main factors that influence fuel consumption for trucks—from major manufacturers such as DAF, Volvo, MAN, Renault, Iveco, Scania, and Mercedes—and six practical methods to reduce consumption.
Factors influencing a truck’s fuel consumption
Average driving speed
Maintaining a steady speed optimizes engine efficiency.
Road conditions
Degraded road surfaces increase rolling resistance.
Truck condition
Regular maintenance ensures optimal functioning of all systems.
Tire condition
Correct tire pressure reduces rolling resistance.
Driving style
Frequent acceleration and braking increase consumption.
Vehicle age
Trucks older than 10 years have significantly higher consumption.
Six effective ways to reduce fuel consumption
1. Checking essential fluids
Before each trip, ensure the levels of essential fluids are optimal:
- Engine oil
- Brake fluid
- Coolant
In cold weather, checking these fluids is even more important, as low temperatures can affect viscosity and efficiency.
2. Monitoring tire pressure
Correct tire pressure is crucial for fuel efficiency. A low pressure:
- Increases rolling resistance, forcing the engine to consume more fuel
- Accelerates tire wear
- Affects stability and handling on the road
- Increases braking distance
During the cold period, tire pressure naturally drops with temperature. Check the pressure regularly and adjust it according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
3. Reducing unnecessary weight
Keep the cab and behind-the-cab area tidy. Avoid carrying unnecessary weight that:
- Increases fuel consumption proportional to the added mass
- Affects vehicle dynamics
- Places more load on the suspension and braking system
Every extra kilogram is reflected in consumption, and over long distances the difference becomes significant.
4. Maintaining a constant speed
Operate with a steady speed to avoid conditions where the engine is underpowered or over-revved. This means:
- Using cruise control on suitable stretches
- Anticipating traffic to avoid hard braking and rapid accelerations
- Keeping the engine in the optimal RPM range (usually between 1200-1600 rpm)
- Shifting to a higher gear as soon as possible
In cold weather, this becomes more challenging due to road conditions (snow, ice), but it remains essential for efficiency.
5. Adopting an economical driving style
Driving style has a major impact on consumption. A preventive and anticipative approach includes:
- Slow, progressive accelerations
- Using engine braking for deceleration
- Anticipating traffic signals and flows
- Avoiding prolonged engine idling
- Reducing cruising speed by 5-10 km/h below the legal limit on highways
Studies show that the difference in consumption between an aggressive driver and a preventive one can reach 30-40%.
6. Regular maintenance and fleet modernization
Trucks older than 10 years have significantly higher consumption due to:
- Wear of mechanical components
- Older engine technology
- Lack of modern engine management systems
- Loss of injector-system efficiency
Preventive maintenance includes:
- Regular replacement of filters (air, fuel, oil)
- Checking and adjusting the fuel-injection system
- Replacing worn components
- Inspecting the exhaust system
Considerations for the cold season
During winter, consumption tends to rise naturally due to:
- Longer engine warm-up times
- Increased rolling resistance on surfaces covered with snow or ice
- Use of additional heating systems
- Higher density of cold air
Adopting all the measures listed above becomes even more important during this period.
Environmental impact
While it would be logical to emphasize reducing fuel consumption to limit pollution with equal weight, auto industry measures mainly aim at CO2 reduction through technologies such as:
- SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) systems
- Particulate filters
- More efficient engines
- Hybrid and electric systems for urban transport
Still, the most direct way to reduce emissions remains lowering fuel consumption through the methods described above.
Conclusion
Optimizing a truck’s fuel consumption is not only about financial savings but also about environmental responsibility and proper vehicle maintenance. Consistently applying these simple measures can lead to fuel savings of up to 15-20%, which on long distances and current fuel prices represents substantial savings.