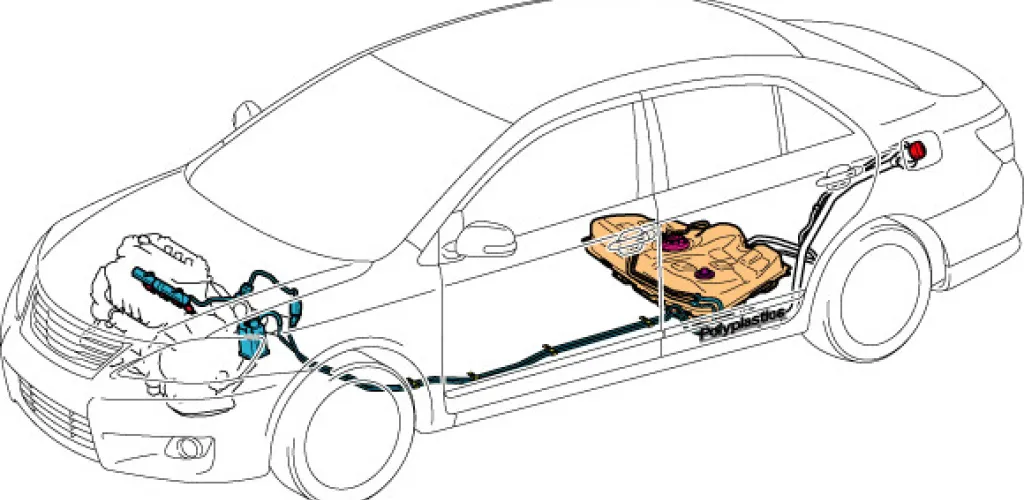
- Regularly inspect tank, lines, connections, and fuel cap for leaks and damage
- Replace air filter at 20,000 km and fuel filter at 20–30,000 km
- Check fuel pump at 100,000 km: pressure, current draw, noises, wiring
- Ensure electrical supply and calibrate MAF and TPS sensors, and check fuel regulator
Maintaining the fuel delivery system is essential for engine reliability and performance. A properly maintained fuel system not only enhances engine efficiency but also helps prevent costly failures over time.
Neglecting fuel system maintenance can lead to serious problems such as injector clogging, fuel pump wear, or even engine damage. Following a preventive maintenance schedule is essential for any vehicle owner.
Tank and fuel line checks
- Visual inspection of the tank for signs of corrosion or damage
- Inspection of the lines for cracks, deformations, or signs of material aging
- Checking the tightness of all connections and fittings
- Testing the fuel cap to ensure a proper seal
Filter maintenance
Air filter
The air filter plays a crucial role in proper engine operation and should be replaced at 20,000 km. A clogged air filter can cause:
- Increased fuel consumption
- Reduced engine power
- Higher emissions
- Premature wear of engine components
Fuel filter
The fuel filter requires replacement at 20,000–30,000 km, depending on the quality of the fuel used and operating conditions. This filter:
- Removes impurities from fuel
- Protects injectors from blockages
- Maintains correct pressure in the system
- Prevents corrosion of components
Fuel pump check
The fuel pump should be checked every 100,000 km. This check includes:
- Testing the pressure generated by the pump
- Checking electrical current draw to detect signs of wear
- Listening for abnormal noises that may indicate mechanical issues
- Inspecting electrical connections and wiring
A faulty pump can cause starting problems, power loss or even engine stalling while driving.
Electrical and electronic checks
Electrical power supply
The modern injection system relies on a stable electrical supply. Check:
- Battery condition and terminal voltage
- Alternator and charging capacity
- Fuses dedicated to the injection system
- Wiring for weak or corroded connections
Sensors and actuators
Electronic components require special attention:
- Mass air flow sensor should be calibrated for precise measurements
- Throttle position sensor requires periodic calibration
- The fuel pressure regulator must be checked and adjusted to the manufacturer’s specifications
Fuel system leak testing
Fuel circuit tightness is crucial for:
- Safety – preventing fuel leaks
- Performance – maintaining correct pressure
- Environmental protection – avoiding pollution
- Economy – reducing fuel losses
Regularly check all fittings, lines and components for signs of leaks or deterioration.
Recommendations for efficient maintenance
Using high-quality fuel
- Refuel at reputable gas stations
- Avoid old or contaminated fuel
- Use additives to help clean the system when necessary
Performance monitoring
- Watch for any changes in fuel consumption
- Pay attention to engine starting
- Monitor exhaust emissions
Preventive maintenance
- Follow the recommended service intervals
- Do not delay replacing filters
- Perform regular checks at specialized service centers
By following these recommendations, you will ensure the optimal operation of the fuel delivery system and prevent costly failures. Proper maintenance not only extends component life but also helps reduce fuel consumption and emissions.
Photo source: polyplastics-global.com