- P0999 signals fault in the F-type solenoid control circuit of automatic transmissions.
- TCM monitors solenoids and disables the F circuit when a fault is detected.
- Causes include wiring deterioration, solenoid faults, control-module issues, and improper repairs.
- Symptoms include inability to engage Drive, stalling in gears, and abrupt shifts.
The P0999 code is one of the more challenging OBD-II trouble codes affecting automatic transmissions. It signals a fault in the F-type solenoid control circuit, a key component for proper transmission operation. Understanding this issue and its remedies is crucial for maintaining vehicle performance and avoiding costly damage.
Transmission issues can turn a smooth driving experience into a costly headache, and the P0999 code is one of the most serious indicators that something is not functioning correctly in your car’s transmission system.
What the P0999 Code Means
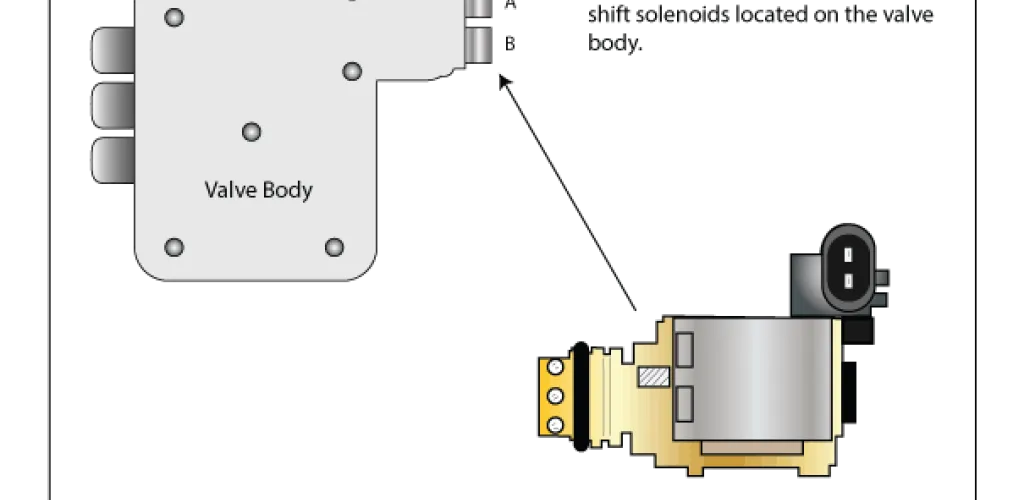
The P0999 code is a generic OBD-II code that identifies a fault in the F-type solenoid control circuit in the automatic transmission. It is stored in the ECM (Engine Control Module) or in the Transmission Control Module (TCM).
Solenoid F is part of the hydraulic control system of the automatic transmission, responsible for engaging and disengaging certain clutches or brakes during gear shifts. When this solenoid is not functioning correctly, the transmission’s operation as a whole can be compromised.
How the Control System Works
The TCM continuously monitors the operation of all solenoids in the transmission by testing electrical resistance and speed sensors. When it detects a fault at the F solenoid circuit, the system automatically disables that circuit to prevent further damage and stores the P0999 code in memory.
Main Causes of P0999
Electrical Wiring Deterioration
One of the most frequent causes is deterioration of the wires that connect the TCM to the F solenoid. This can result from:
- Wire corrosion - exposure to moisture and road salt can corrode connections
- Mechanical wear - engine vibrations can cause chafing and wire breakage
- Rodent damage - mice and other small animals can gnaw on insulation
- Aging materials - the vehicle’s age can lead to natural insulation deterioration
Solenoid Failures
The F solenoid itself may have the following problems:
- Wear of the electromagnetic coil - electrical resistance can become improper
- Mechanical sticking - metal particles or dirt can block the solenoid piston
- Seal damage - internal leaks can affect hydraulic pressure
Control Module Issues
- TCM failure - the transmission control module may have blown components
- ECM issues - the engine control module may send incorrect signals
- Electromagnetic interference - other vehicle systems may interfere with signals
Improper Repairs
Previous mechanical interventions can cause the issue:
- Incorrect reconnection of wires after radiator or engine repairs
- Use of non-original parts that do not meet specifications
- Low-quality repair kits
Symptoms of the P0999 Code
Severe Operational Problems
- Inability to engage Drive (D) mode - the most severe consequence
- Stalling in certain gears - the transmission remains locked in gear like 2 or 3
- Abrupt speed changes - shifts between gears become uncontrollable
- Clutch slipping - loss of traction in certain conditions
Secondary Symptoms
- Poor acceleration - the vehicle does not respond to throttle input
- High engine RPMs without proportional acceleration - the engine revs high without corresponding speed
- Increased fuel consumption - fuel efficiency drops significantly
- Transmission overheating - transmission oil temperature rises
Diagnosing the Problem
Equipment Needed
For accurate diagnosis you will need:
- Professional OBD-II scanner - for reading codes and real-time parameters
- Digital multimeter - for measuring resistance and voltage
- Vehicle electrical schematics - specific to the make and model
- Test probes set - for accessing difficult connectors
Diagnostic Steps
Preliminary checks:
- Read all active and pending trouble codes
- Check the history of codes for recurring issues
- Test transmission fluid level and quality
Electrical testing:
- Measure the resistance of the F solenoid (usually 12-25 ohms)
- Check continuity of the wiring between the TCM and solenoid
- Test the supply voltage (usually 12V)
- Inspect the circuit grounding
Functional testing:
- Monitor TCM signals in real time with the scanner
- Test the solenoid response to commands
- Check hydraulic pressure in the respective circuit
Repair Methods
Wiring Repair
- Replacing damaged sections with wires of the same specification
- Repairing corroded connections with specialized cleaning products
- Protecting the wiring with flexible conduits to prevent future damage
- Inspecting and tightening all connectors
Replacing the Solenoid
Procedure includes:
- Drain transmission oil
- Remove the lower transmission pan
- Locate and disconnect the F solenoid
- Install the new solenoid with the specified torque
- Refill with fresh oil and test the system
Control Module Repairs
In rare cases, it may be necessary to:
- Reprogram the TCM with the latest software
- Replace the TCM module if permanently faulty
- Check and repair the ECM if the issue originates there
Preventive Maintenance
To avoid recurrence:
- Regular transmission fluid changes per the maintenance schedule
- Use the oil recommended by the manufacturer
- Periodic checks of electrical connections
- Keep the vehicle in a clean and dry environment when possible
Severity of the Issue
Safety Risks
- Unexpected vehicle stoppage in traffic
- Loss of traction power in critical situations
- Unpredictable changes in vehicle behavior
Potential Mechanical Damage
- Accelerated wear of transmission components
- Engine overrevving due to high RPMs
- Damage to the torque converter
- Differential problems
Repair Costs
Ignoring this code can lead to:
- Complete transmission rebuild — 15,000-30,000 RON
- Transmission replacement — 20,000-40,000 RON for newer vehicles
- Engine damage due to overloading — substantial additional costs
Recommendations for Vehicle Owners
When Symptoms Appear
- Stop the vehicle safely at the first sign of serious trouble
- Avoid aggressive driving or long trips
- Contact a specialized service center as soon as possible
- Do not ignore the vehicle’s warning systems
Preventive Maintenance
- Follow the transmission fluid change intervals
- Use only genuine or quality-equivalent parts
- Perform periodic checks on electrical systems
- Keep the vehicle in a clean and dry environment when possible
Choosing a Service
For repairing this complex issue, it is essential to choose a service that:
- Has specific experience with automatic transmissions
- Uses modern diagnostic equipment
- Offers warranty on the work performed
- Uses quality guaranteed replacement parts
P0999 requires a professional approach and should not be underestimated. A prompt and correct intervention can save the vehicle’s transmission and prevent exorbitant repair costs in the long term.