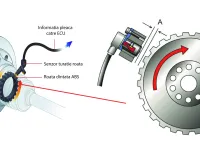
- TPS provides direct signal to fuel-injection system about throttle demand
- It can fail gradually or abruptly, often triggering the Check Engine light
- Signs include reduced acceleration, power loss, and idle instability
When the throttle position sensor (TPS) begins to malfunction, your car will display a variety of performance issues affecting both driving comfort and road safety. These symptoms range from power loss to rough acceleration to serious idle-related engine problems.
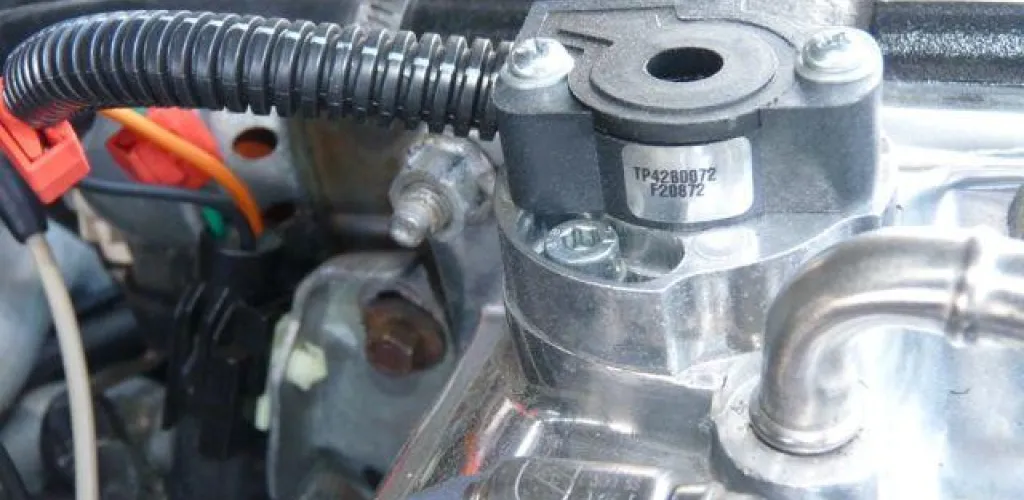
The TPS is a crucial component of the engine management system, responsible for transmitting precise information about the throttle pedal position to the electronic control unit (ECU). When this sensor fails, the entire fuel delivery system is affected.
The role of the throttle position sensor (TPS)
The throttle position sensor (TPS) is part of the vehicle’s fuel-management system and helps ensure the correct air-fuel mixture reaches the engine.
TPS provides the most direct signal to the fuel-injection system regarding the power demands the engine places on it. The sensor position signal is measured continuously and is combined many times per second with other data, such as:
- Intake air temperature
- Engine RPM
- Mass air flow (MAF)
- Throttle position change rate
These data determine exactly how much fuel is injected at any moment. If the TPS sensor and other sensor parameters operate correctly, the car accelerates smoothly, cruises easily at cruising speed, or decelerates without problems and while maintaining optimal fuel economy.
TPS sensor failure modes
The throttle position sensor can fail in several ways, all resulting, at best, in insignificant fuel economy and at worst, in performance limitations that could pose a safety risk to you and other vehicles on the road.
It can also cause issues with gear changes or with setting the base ignition timing of the spark produced by spark plugs. The TPS sensor can fail gradually or will manifest all the listed problems simultaneously.

In most cases, the Check Engine light comes on if a TPS fault is detected. Also, most manufacturers provide a safety-map-enabled operating system that limits engine performance when faults occur.
Main signs of TPS sensor failure
1. Acceleration and power issues
It may feel as if the car simply does not accelerate as it should, or as you increase speed, it does not respond as expected. You can accelerate, but the engine lacks power.
On the other hand, the car may surge forward while you are driving, even if you have not pressed the accelerator pedal. If these symptoms appear, there is a high probability you have a TPS position sensor problem.
These manifestations occur because the ECU receives erroneous information about the driver’s demand, resulting in incorrect fuel metering.
2. Idle instability
If you start experiencing engine faults, very slow idle, or idle irregularities when the vehicle is stopped, this can also be a warning sign of a faulty TPS sensor.
If the idle is unstable, it means the computer cannot identify whether the throttle is fully closed. Also, the TPS can send an incorrect input pulse, resulting in the engine stopping at any moment.
3. Speed limiting and shifting issues
This is another mode of TPS failure, indicating a false limit on the requested speed. Your car may accelerate but fail to exceed 30–50 km/h. This fault indicator often goes hand in hand with power loss.
This problem occurs because the ECU, to protect the engine, limits performance when it detects inconsistent signals from the TPS sensor.
4. Check Engine light on
The Check Engine light can come on if you have TPS sensor problems. This is not always the root cause, so don’t wait for the engine check light to come on before verifying any of the above symptoms.
Check your vehicle’s error codes to identify the source of the problem. Common codes associated with TPS faults include:
- P0120 - Throttle Position Sensor circuit
- P0121 - TPS performance/range
- P0122 - TPS signal low
- P0123 - TPS signal high

Diagnosing and replacing the TPS sensor
Once the TPS begins to malfunction, you should replace it promptly. Replacing the TPS sensor will include erasing the relevant error codes and may require reprogramming the software of the new sensor module to synchronize with other engine controls.
A qualified mechanic is able to perform all necessary procedures, provide a quality diagnostic, and then carry out the correct installation of the replacement part.
The diagnostic process includes:
- Scanning error codes with a professional automotive tester
- Checking the sensor supply voltage (usually 5V)
- Testing the output signal at different throttle positions
- Checking circuit continuity of electrical wiring
- Visual inspection for corrosion or physical damage
The importance of a quick repair
The throttle position sensor is the key to obtaining the power and fuel efficiency you want from your vehicle in any driving situation. As the signs above show, if this part fails, your safety on the road is seriously compromised and a check by a qualified mechanic is essential.
Ignoring TPS sensor issues can lead to:
- Catalytic converter damage due to an improper air-fuel mixture
- Premature engine wear
- Increased fuel consumption
- Increased risk of an accident due to power loss in traffic
To avoid these serious problems, it is essential to promptly address any suspicious symptoms related to TPS sensor operation.
Sursa foto: fuelpumpu.com, americanmuscle.com, paulsgiganticgarage.com, mikeshawsubaru.com