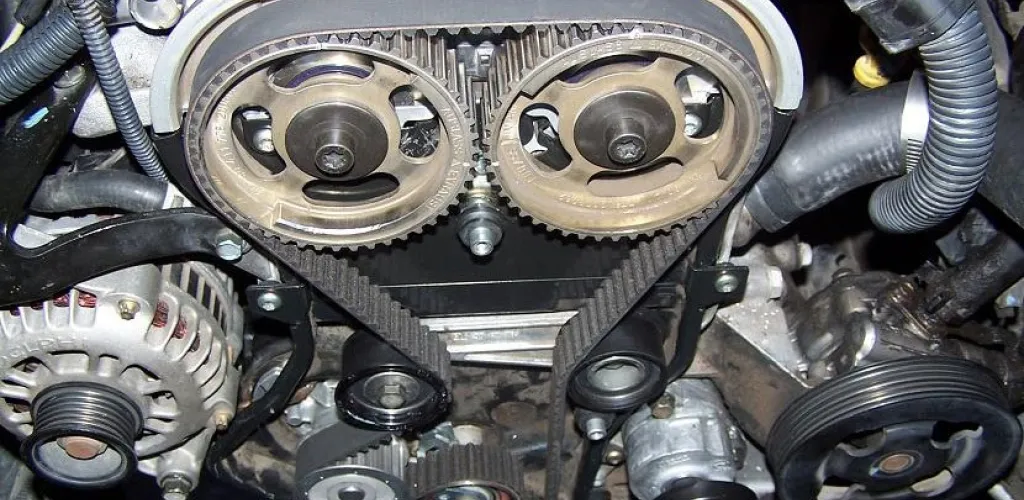
- Warning signs include unusual engine noises, misfires, starting problems, and oil leaks near the belt.
- Timing belt synchronizes crankshaft and camshaft; replacement intervals vary 40k-150k km.
- Belt slip can cause engine failure and major damage.
The timing belt is one of the most critical components of a modern engine, and recognizing signs of wear early can prevent major and costly damage. The most common indicators that this belt is no longer functioning correctly include unusual engine noises, misfires, starting problems, and oil leaks around the belt area.
Ignoring these signs can lead to serious engine damage with repair costs that may surpass the vehicle’s value in extreme cases. Therefore, understanding how this component works and recognizing wear signs are essential for every vehicle owner.
What is the timing belt and its role
Timing belt represents a vital internal component that synchronizes the rotation of the crankshaft with the camshaft, ensuring ignition for each cylinder at the exact moment. Located behind a protective cover at the front of the engine, this belt is subjected to extreme mechanical stresses during operation.
Made of high-quality rubber and internally reinforced with nylon fibers for added strength, the timing belt is designed to withstand extreme temperatures and intense mechanical loads. However, like any wear-prone component, it will require replacement at regular intervals to prevent engine damage.
Difference between timing belt and timing chain
Depending on the engine type and capacity, manufacturers choose between two timing solutions: the belt or the chain. Engines with smaller displacement typically use timing belts, while engines with larger bore and longer stroke are equipped with timing chains.
Timing chains offer greater durability, with many operating for the life of the engine. Belt replacement intervals vary between 40,000 and 150,000 km, depending on manufacturer specifications and operating conditions.
Main warning signs
Characteristic engine noises
One of the first signs of a worn timing belt is the appearance of a distinctive ticking sound coming from the engine area. This noise occurs because the belt, connected by pulleys to the camshaft and the crankshaft, begins to lose optimal tension or develop cracks.
The ticking noise can also indicate other related issues:
- Low engine oil pressure
- Inadequate lubrication of components
- Wear of pulley bearings
- Failure of belt tensioners
- Wear of belt guide pulleys
Given the critical importance of this component, any unusual noise requires immediate professional inspection.
Starting problems
When the timing belt slips completely, the engine can no longer start, even if the starter motor functions normally. This happens because the synchronization between the crankshaft and the camshaft is compromised, making engine operation impossible.
If the belt slips while the engine is running, the consequences can be devastating, including:
- Avaries in cylinder systems - piston and combustion chamber deformation
- Deterioration of the crankshaft - wear of bearings and journals
- Oil pump failures - loss of lubrication pressure
- Valve train problems - valve, tappet, and cam follower damage
- Piston damage - particularly for interference engines
Misfires and irregular operation
A partially worn belt can begin to slip on pulleys, affecting valve timing. This desynchronization causes misfires and irregular engine operation, manifested by:
- Abnormal vibrations – felt in the steering wheel and pedals
- Power loss – weak acceleration and delayed response
- Increased fuel consumption – inefficient combustion
- Significantly higher emissions – failure in official emission tests
- Unstable idle – engine stalls frequently
Ignoring these symptoms can lead to permanent engine damage and prohibitive repair costs.
Oil leaks around the timing area
Oil leaks from the timing belt cover indicate issues. These leaks can be caused by:
- Loose mounting hardware – bolts that have loosened
- Worn gaskets – deterioration of seals between block and cover
- Incorrect installation – faulty mounting at non-specialized service
- Aging materials – elastomers that have lost flexibility
Consequences of the leaks include:
- Higher operating temperature
- Accelerated belt wear
- Contamination of other components
- Risk of fire in extreme cases
- Environmental pollution
Additional signs to monitor
Excessive vibrations in the vehicle
An over-tensioned or partially damaged belt generates vibrations that travel through the vehicle. These are more noticeable under acceleration and can affect driving comfort and steering stability.
Rubber debris in the engine area
Presence of rubber fragments around the timing cover indicates advanced belt wear. These fragments can contaminate engine oil and other fluids, worsening existing issues.
Changes in engine sound
Changes in the tone and intensity of the engine sound can signal timing problems caused by a faulty belt. An engine that sputters or idles unevenly requires immediate attention.
Factors accelerating belt wear
Operating conditions
- Extreme temperatures – excessive heat and severe cold accelerate rubber deterioration
- High humidity – promotes corrosion of associated metal components
- Dust and impurities – enter the system and act as abrasives
- Engine vibrations – unbalanced engines over-stress the belt
Maintenance factors
- Inadequate lubrication – old or poor-quality oil affects all components
- Overdue service intervals – neglecting periodic checks
- Non-conforming replacement parts – using inferior components
- Incorrect installation – improper tensioning or misalignment
Driving style
- Heavy urban traffic – frequent stops and starts
- Sport driving – extreme engine loading
- Overloading the vehicle – exceeding recommended limits
- Neglected maintenance – postponing scheduled services
Prevention strategies
Systematic preventive maintenance
Strict adherence to the manufacturer’s recommended replacement intervals is the most effective preventive method. These intervals are derived from extensive testing and take standard operating conditions into account.
Regular checks necessary:
- Check engine oil level and quality every 1,000 km
- Monitor engine temperature during driving
- Visual inspection of the engine area for signs of leaks
- Listen for unusual noises
Associated components to replace
When changing the timing belt, experts recommend simultaneous replacement of:
- Timing belt tensioner
- Guiding and deflection pulleys
- Water pump – in many cases driven by the same belt
- Gaskets and seals
- Engine oil – to remove contaminants
This holistic approach prevents premature failure of the new belt and ensures optimal long-term operation.
Economic aspects and costs
Estimated replacement costs
Costs vary significantly depending on multiple factors:
Main factors that influence price:
- Vehicle make and model
- Engine complexity and accessibility of components
- Quality of parts used (OEM vs aftermarket)
- Service rate charged
- Need for replacement of associated components
Cost range:
- Simple replacement: 800-1,500 RON
- Replacement with associated components: 1,500-3,000 RON
- Repairs after belt failure: 5,000-15,000 RON
- Complete engine rebuild: 10,000-25,000 RON
Cost-benefit ratio
Investing in preventive belt replacement represents a fraction of the cost of major repairs. A damaged engine due to belt failure may require:
- Cylinder head and block repair
- Piston and connecting rod replacement
- Crankshaft repair or replacement
- Rebuilding the lubrication system
In many cases, repair costs exceed the vehicle’s value, making preventive replacement a wise investment.
Recommendations for vehicle owners
Active monitoring
Develop a monitoring routine that includes:
- Careful listening to the engine at each start
- Observing changes in the vehicle’s behavior
- Periodic visual checks of the engine area for signs of trouble
- Keeping a mileage log for service intervals
Choosing the right service
Selecting a specialized service is crucial for:
- Accurate problem diagnosis
- Using the right parts and oil
- Following proper installation procedures
- Providing warranty for the work performed
Documenting interventions
Keep a detailed record of all timing belt interventions, including:
- Date and mileage at replacement
- Brand and specifications of parts used
- Service provider that performed the work
- Warranties offered
These records are valuable for preventive maintenance and can influence the vehicle’s resale value.
Conclusion
Early recognition of timing belt wear signs can prevent catastrophic damage and save substantial costs. The most important indicators — unusual noises, starting problems, misfires, and oil leaks — should never be ignored.
Preventive maintenance, adherence to replacement intervals, and choosing a specialized service are investments small compared with the costs of major repairs. A responsible owner will actively monitor these signs and act promptly at the first sign of trouble.
Final recommendation: At the first sign of a timing belt problem, contact a specialized mechanic immediately. The time saved by delaying intervention can cost tens of times more than timely preventive replacement.