- DPF is required by Euro 5; removing it may have legal implications.
- Removal can be hardware-based or ECU reprogramming.
- Fuel economy can improve 5-15%, with 10-25 hp and 30-50 Nm torque gains.
- Removal improves exhaust flow, reduces backpressure, improves responsiveness, and lowers temperatures.
The Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) is one of the most discussed components in the automotive community, raising questions about its impact on vehicle performance. Many diesel car owners wonder whether removing this system can improve engine power and reduce maintenance costs.
Since 2009, under European Euro 5 regulations, all diesel vehicles must be equipped with a DPF. While this system plays a crucial role in reducing pollution, many drivers believe it negatively affects their vehicle’s performance.
What is the DPF filter and how it works
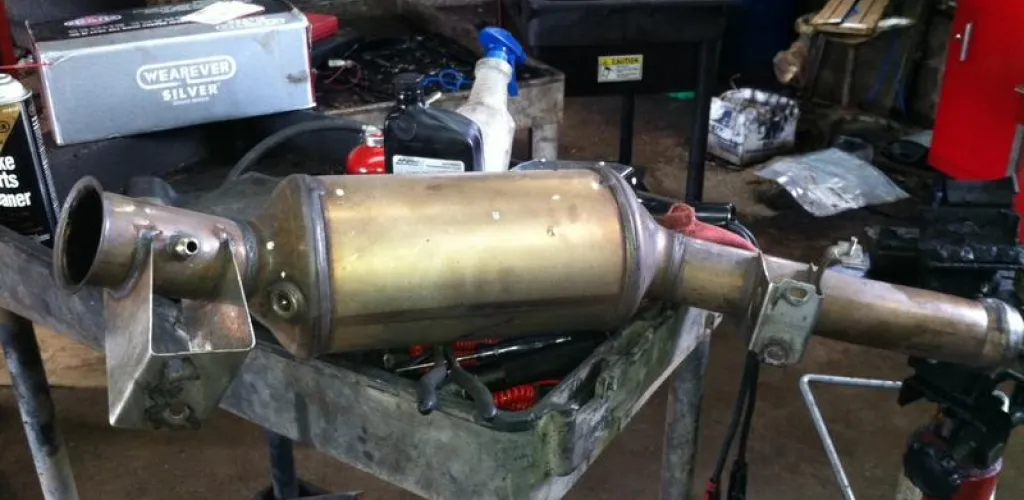
As the name suggests, the DPF is mounted on the vehicle’s exhaust system and has the role of filtering emissions to capture soot and carbon deposits produced by the engine. The captured soot is stored in a special compartment in the exhaust system.
When this compartment fills, the system automatically initiates a regeneration cycle. The process involves burning the accumulated soot using a small amount of additional fuel and removing the resulting gases. This regeneration can be:
- Passive: performed automatically at high exhaust gas temperatures
- Active: the system injects additional fuel to raise the temperature
- Forced: requires service intervention with specialized equipment
DPF removal process
Hardware modification
Traditionally, removal is done by physically removing the filter from the exhaust system. For those seeking a more aesthetic solution, there are special exhausts that physically replace the DPF, maintaining the original appearance of the system.
Software reprogramming
The tuner disables the software by configuring the engine codes in the onboard computer (ECU). This modification is essential so that the system operates without errors after the physical removal of the filter.
Advantages of DPF removal
Improved fuel economy
A clogged or worn DPF significantly slows exhaust gas flow, creating backpressure in the system. This backpressure forces the engine to work harder to evacuate gases, resulting in higher fuel consumption.
By removing the DPF:
- The gas flow becomes smoother and more constant
- Backpressure in the exhaust system is reduced
- The engine runs more efficiently
- Fuel economy can improve by 5-15%
Increase in engine power
Removing the DPF can have the following effects on performance:
Improved air flow: A freer exhaust allows more efficient expulsion of burnt gases, improving cylinder filling with fresh charge.
Lower temperatures: Without regeneration cycles, temperatures in the engine compartment stay lower, protecting components.
Improved responsiveness: The engine becomes more responsive to acceleration, removing delays caused by the DPF system.
Depending on the engine, power gains can be between 10-25 hp, and torque can increase by 30-50 Nm.
Reducing maintenance costs
DPF filters require regular maintenance, especially for vehicles that travel over 15,000-20,000 km per year:
- Professional cleaning: 300-800 RON every 30,000-50,000 km
- Replacing the filter: 3,000-8,000 RON depending on model
- Sensor maintenance: 200-500 RON for faulty sensors
- Related issues: turbocharger, EGR, injectors affected by repeated regenerations
Disadvantages and risks of removing the DPF
Environmental impact
Removing the DPF eliminates the vehicle’s ability to filter fine particulates, significantly increasing pollutant emissions. A DPF-less vehicle emits 10-20 times more particles than one equipped with a functioning filter.
Legal implications in Romania
Removing the DPF is illegal under current legislation:
RAR penalties:
- License plate seizure
- Seizure of the registration certificate
- Fine of 1,305-2,900 RON
- Obligation to reinstall the system for re-homologation
ITP implications:
- Rejection at the periodic technical inspection
- Inability to renew the ITP without reinstalling the DPF
Potential technical issues
Affecting other components: Without the DPF, the EGR system and the turbocharger can be affected in the long term due to altered gas flows.
Diagnosis problems: Incorrect removal can generate persistent errors in the engine management system.
Legal alternatives to DPF removal
Preventive maintenance
- Regular highway driving to allow natural regeneration
- Using fuel additives
- Regular professional cleaning
Legal modifications
- ECU remapping to optimize regeneration
- Replacing with a higher-quality aftermarket DPF
- Upgrading to an approved sport exhaust system
Conclusion
Although DPF removal can bring notable improvements in engine power, fuel economy, and maintenance costs, this modification remains illegal and may have serious legal consequences. Power gains of 10-25 hp and fuel economy improvements of 5-15% must be weighed against legal risks and environmental impact.
Before making such a decision, it is essential to carefully evaluate all aspects: technical benefits, legal risks, environmental impact, and legal alternatives available. For most owners, proper maintenance of the DPF system represents a safer and more responsible long-term solution.