- Remote sends a coded radio signal to the car’s central receiver.
- Central receiver decodes signals and commands door actuators.
- Actuators use a motor and rod to lock or unlock doors.
- Keyless entry uses RFID or proximity with 1-2 m range and automatic locking.
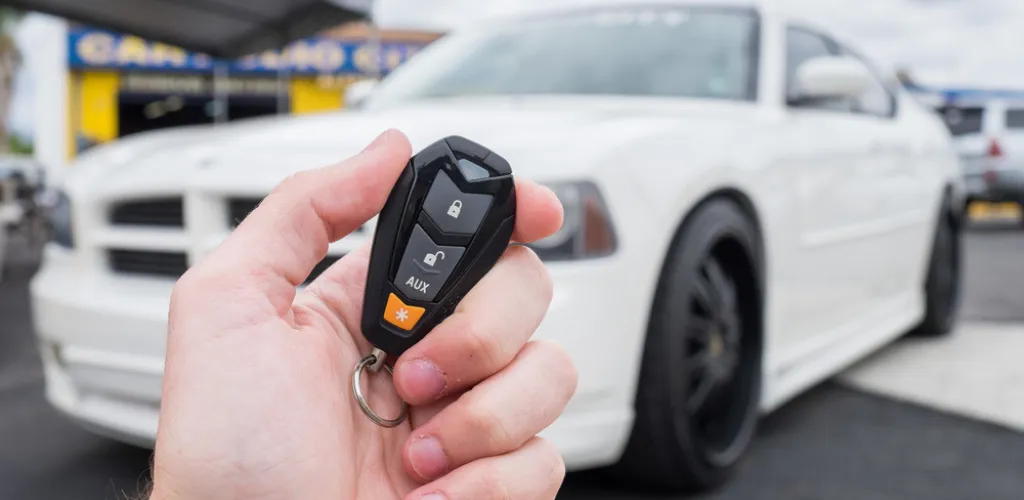
Central locking is one of the most widely used technologies in modern cars, offering comfort and safety through the electric control of all vehicle locks. This complex mechanism relies on radio-wave communication between the remote control and the actuators mounted on each door, allowing the entire vehicle to be locked or unlocked with a single press of a button.
Understanding how this system works can be useful for diagnosing problems as well as understanding the limits and possibilities of your car’s technology.
Main components of the system
Transmitter (remote)
The car’s remote functions as a low-power radio transmitter, usually on the 433 MHz or 868 MHz frequency. It contains:
- An electronic circuit with a unique identification code
- A small battery (usually CR2032 or similar)
- Buttons for different functions (lock, unlock, trunk)
- A miniature antenna for signal transmission
Central receiver
Mounted in the vehicle, this module receives and decodes signals from the remote. It verifies the security code and transmits commands to the corresponding actuators.
Door actuators
Each door is equipped with an electric actuator that converts the electrical signal into mechanical motion.
How the actuator works in detail
The actuator is the heart of the central locking system and operates on simple yet effective electromechanical principles.
Transmission and reception process
When you press the button on the remote, the following sequence is triggered:
- Signal generation: The remote generates a coded radio signal specific to your vehicle
- Transmission: The signal is transmitted by radio waves to the vehicle’s receiver
- Decoding: The control module checks the code and confirms the signal authenticity
- Activation: Commands are sent to the corresponding actuators
Actuation mechanism
The actuator contains a small electric motor and a transmission system that moves a metal rod connected directly to the door locking mechanism. This rod exerts the pressure necessary on the switch that controls the lock position – closed or open.
The motor can operate in both directions, allowing both locking and unlocking of the doors by reversing the current polarity.
Advanced keyless entry systems
For keyless cars, the central locking technology is more sophisticated. These systems use RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology or proximity magnetic field communication.
How the keyless system works
- Key detection: Strategically placed sensors around the vehicle continuously monitor the presence of the key
- Range: Typically between 1-2 meters from the vehicle
- Automatic activation: On approaching the car, the system activates automatically
- Automatic locking: When moving away with the key, the vehicle can auto-lock after a preset interval
Advantages of keyless technology
- Increased comfort – no need to take the key out of your pocket
- Enhanced security through encrypted codes
- Additional features such as keyless engine starting
Common problems and solutions
Dead battery
If the car’s battery dies or the key’s battery dies, the central locking system will not function. It is important to:
- Check the owner’s manual for the emergency opening procedure
- Keep a spare battery for the remote
- Know the location of the mechanical lock (usually hidden in the door handle)
Signal problems
- Radio interference in urban areas
- Distance too far from the vehicle
- Damage to the receiver antenna
Mechanical faults
- Wear of actuators over time
- Rods jamming due to dirt or corrosion
- Issues with door switches
System maintenance
To keep the system in optimal working condition:
- Regular cleaning of contacts in the remote
- Annual battery check for the remote
- Lubrication of locking mechanisms
- Periodic testing of all doors

Evolution of technology
Modern central locking systems have evolved significantly, integrating with other vehicle systems:
- Mobile app connectivity
- Integration with alarm systems
- Geolocation features
- Control via voice assistant
Understanding these technical principles helps you use your car’s system more effectively and quickly identify potential issues that may arise in operation.