- Car batteries typically last 3–5 years, depending on use, quality, and maintenance.
- Signs of failure include hard starting, low power, intermittent electricals, and dim lights.
- Winter reduces performance; aging plus cold can cause failures.
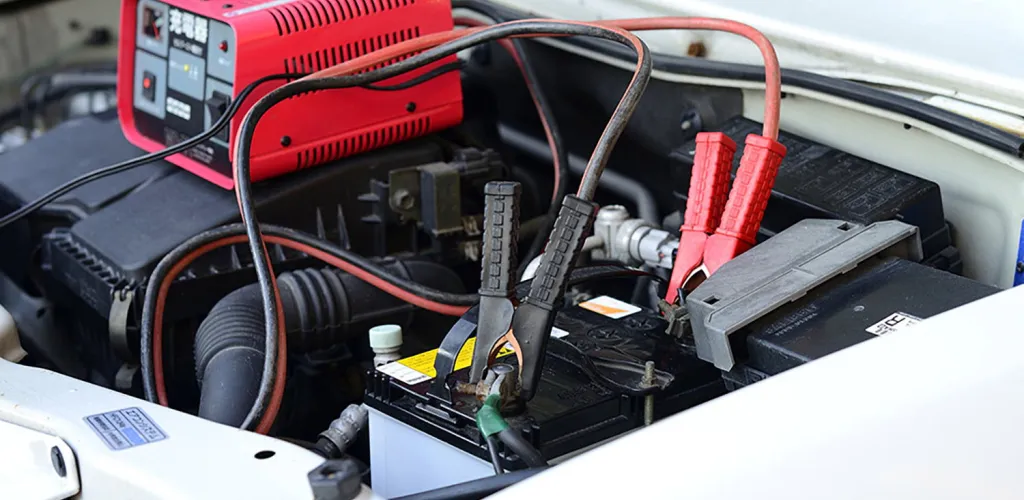
- Rapid recharge methods: jump-starts, portable starters, or overnight battery chargers.
An automotive battery can last between 3 and 5 years, depending on several key factors. The frequency of vehicle use, battery quality, and maintenance conditions directly influence the lifespan of this essential component. Vehicles used several times a week, under optimal driving conditions, can keep the same battery functional for up to five years. In contrast, cars that sit idle for long periods and are not started regularly may require a new battery after only three years.
Signs the car battery is failing
Early recognition of failure signs can prevent unpleasant situations. The most common indicators that the battery is about to give out include:
- The engine starts with difficulty
- The engine does not have enough power when turning the key
- The vehicle’s electrical systems operate intermittently
- Dashboard lights flicker or dim in intensity
Most batteries show signs before they completely discharge, giving you time to take action. However, some batteries can fail abruptly, especially under extreme temperature conditions.
Impact of low temperatures
In winter, low temperatures significantly affect battery performance. The chemical reactions inside the battery occur more slowly in the cold, reducing the current delivery capacity required to start the engine. If your battery is already a few years old, the combination of aging and low temperatures can lead to failures.
Repair or replacement - which option to choose
The decision between repairing and replacing the battery depends on the cause of the discharge and the age of the component. In some situations, the problem is not the battery itself, but external circumstances:
- Radio or lights left on overnight
- Extremely low temperatures
- Prolonged period of non-use of the vehicle
- Parasitic draw caused by defective electronic equipment
Rapid recharge methods
When the battery discharges for circumstantial reasons, recharging is the first solution to try:
Jump-start cables: Connect the discharged battery to a functional battery on another vehicle. Make sure you observe the correct polarity - red to positive, black to negative. Let the donor car run for a few minutes before attempting to start the vehicle with the discharged battery.
Portable battery starter: A portable jump starter is a useful investment for emergencies. These compact devices can start most vehicles and do not require the presence of another car.
Battery charger: For a full and gentler recharge, use a specialized charger overnight. This method is ideal if you have time and access to an electrical outlet.
Solutions for frequent discharges
Service checks
A specialized workshop can diagnose causes such as:
- Alternator failures that do not recharge the battery while driving
- Current leaks caused by faulty electrical circuits
- Electrical consumers that remain active after the engine is turned off
- Problems with the voltage regulator
- Corroded terminals or loose connections at the battery posts
Proper battery maintenance
To maximize battery life, follow these practices:
- Clean the terminals regularly: Corrosion at the connections reduces the efficiency of current transfer
- Check the electrolyte level: For maintenance batteries, top up with distilled water when necessary
- Test the voltage periodically: A healthy battery reads about 12.6V at rest
- Avoid complete discharges: These significantly reduce battery life
Tips for periods of non-use
Important: If you do not use the car for periods longer than two weeks, disconnect the battery to prevent discharge. Start with the negative terminal to avoid short circuits. This simple measure can significantly extend the battery’s life and ensure the car will start when you need it.
Alternative, you can invest in a maintenance charger (trickle charger) that keeps the battery at the optimal charging level without the risk of overcharging.
When it’s time to replace the battery
Even with proper maintenance, a car battery has a limited lifespan. Consider replacing when:
- The battery is more than 4-5 years old
- Capacity tests show below 50% of nominal capacity
- Frequent discharges continue after service checks
- The battery casing shows bulging or cracks
- There are acid leaks or excessive corrosion
Investing in a higher-quality battery may seem expensive at first, but it pays off through reliability and longer life. Always choose a battery with the vehicle manufacturer’s recommended specifications for capacity (Ah) and cold-cranking amps (CCA).