- Battery condition, capacity, charger type, and conditions determine charging duration
- For 40Ah, 2A takes 10-15 hours; 15A takes 1-2 hours
- Discharge causes include forgotten loads, excessive draw, faults, and cold conditions
- Warning signs include hard starts and dim dashboard; temperature and age affect charging
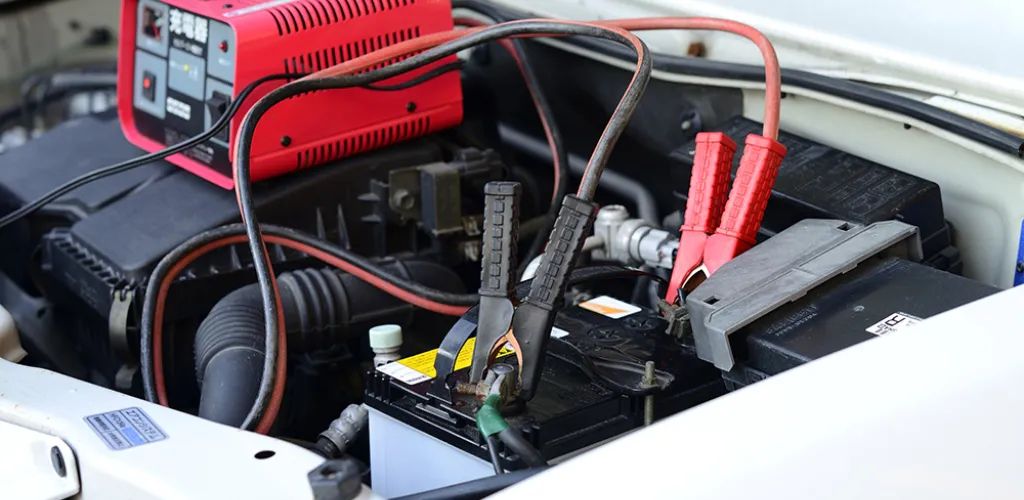
Every driver has faced at least once the situation where their car battery is discharged. Whether due to aging or because a forgotten accessory drained the battery, the result is the same: the car won’t start.
The charging time for a car battery varies significantly depending on several factors: the battery’s current state, its capacity, the type of charger used, and external conditions. A 2-amp charger will require 10-15 hours for a 40Ah battery, while a 15-amp charger can finish the process in just 1-2 hours.
Role and Importance of the Car Battery
Batteries play a crucial role in the life of any vehicle, because:
- Provides the energy needed to start the engine
- Stores energy and is directly connected to the alternator
- Powers all electrical loads when the engine is not running
- Ensures the operation of safety and comfort systems
A discharged car battery will not allow us to operate most electrical loads or crank the engine, so it is very possible to be stranded until we manage to charge the battery.
Main Causes of Battery Discharge
Forgotten loads left on
- Headlights left on overnight
- Interior lights left on
- Radio or navigation system running with the engine off
- Phone chargers plugged into the 12V outlet
Excessive use of electrical loads
When we use several loads at the same time (radio, headlights, phone charging) with the ignition on but the engine not running, the alternator does not recharge the battery, and loads can drain it quickly.
Common technical faults
- Alternator underperforms or is faulty
- Current leaks in the electrical system
- Voltage regulator problems
- Corrosion at the battery terminals
Unfavorable operating conditions
- Short trips with low speeds
- Long periods of vehicle inactivity
- Very low temperatures (reduce battery capacity by up to 50%)
- Old and worn-out battery that no longer holds a charge
Warning signs
Recognize battery problems early with these symptoms:
- Difficult engine start
- Dashboard lights dim or flicker
- Headlights dimmer at idle
- Electrical systems operate intermittently
- Error messages on the dashboard
Factors Affecting Charging Duration
Current state of the battery
- Current state of charge (can be tested with a voltmeter)
- Age and degree of wear
- Ability to hold a charge
Technical specifications
- Total capacity expressed in Ah (ampere-hours)
- Nominal voltage (12V for passenger cars)
- Battery type (classic lead-acid, AGM, gel)
Charging equipment
- Charger power (expressed in amps)
- Charger type (simple or smart with microprocessor)
- Quality of cables used
External conditions
- Ambient temperature (optimal: 15-25°C)
- Humidity in the working area
- Proper ventilation
Charging Times by Equipment
Estimated durations table
| Charger | 40Ah Battery | 60Ah Battery | 80Ah Battery |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 amps | 10-15 hours | 15-20 hours | 20-25 hours |
| 6 amps | 4-6 hours | 6-8 hours | 8-10 hours |
| 10 amps | 2-3 hours | 3-4 hours | 4-5 hours |
| 15 amps | 1-2 hours | 2-3 hours | 3-4 hours |
Technical note: Most modern chargers are “smart”, meaning they adjust the charging rate as the battery fills. Therefore, the above calculations are approximate, as the charging rate will slow down as you approach a full 100% charge.
Charging Methods for the Car Battery
Charging with a charger (external charger)
Advantages:
- Controlled and safe charging
- Does not affect other vehicles
- Allows slow charging (recommended for longevity)
- Precise control over parameters
Disadvantages: -Requires access to electrical mains
- Longer duration
- May require removing the battery
Step-by-step procedure:
- Turn off the engine and remove the key from the ignition
- Disconnect the battery terminals (first the negative, then the positive)
- Clean the terminals of corrosion with a wire brush
- Connect the charger (red to positive, black to negative)
- Set correct parameters on the charger (voltage and current)
- Monitor the charging process
Jump-start with cables
Advantages:
- Quick solution for emergencies
- Does not require mains power
- Enables immediate starting
Disadvantages:
- Requires another functioning vehicle
- Risk of damage to sensitive electronics
- Does not solve the long-term problem
Correct safety procedure:
- Position the vehicles close but do not touch
- Both engines off, handbrake engaged
- Connect the cables in this order: positive to positive, then negative to the chassis/ground
- Start the donor vehicle and let it run for 2-3 minutes
- Try to start the vehicle with the discharged battery
- Disconnect the cables in reverse order
Charging by driving
Necessary conditions:
- The battery must have enough energy to start the engine
- The alternator must be functional
- Driving with engine speeds above 2000 rpm is recommended
Estimated duration:
- 30-60 minutes for partial charging (50-70%)
- 2-3 hours for full charging through active driving
Slow Charging vs. Fast Charging
Slow charging (2-6 amps)
Benefits:
- Recommended for long-term battery health
- Generates less heat
- Extends life by up to 30%
- Ensures full and even charging of all cells
Fast charging (10+ amps)
Characteristics:
- Useful in emergencies
- Generates excessive heat (over 45°C can be detrimental)
- May affect life expectancy by damaging active plates
- Does not always ensure full charging of all cells
Essential Safety Measures
Protective equipment
- Protective gloves against sulfuric acid
- Safety glasses to prevent splashes
- Appropriate clothing (avoid synthetic fabrics)
Precautions during charging
- Ensure proper ventilation (batteries emit hydrogen)
- Do not smoke near the battery
- Check cable condition before use
- Do not leave the charger unattended for long periods
- Avoid sparks near the terminals
What to Do After Charging
You should drive the car for 20-30 minutes after disconnecting the battery from charging. This allows the alternator to:
- Refill the battery to optimal parameters
- Stabilize the electrical system voltage
- Test operation under real-use conditions
- Balance the battery cells
If you stop the vehicle after only 5 minutes, there is a good chance the battery will discharge again, not having enough time to accumulate sufficient energy for the next start.
When to Replace the Battery
Clear signs of replacement
- Age over 4-5 years (3-4 years in extreme conditions)
- Drains frequently without an apparent reason
- Charging time has increased significantly
- Visible cracks or leaks
- Capacity test shows below 80% of nominal value
- Terminals are excessively corroded and cannot be cleaned
Professional battery health testing
With a digital voltmeter:
- 12.6V or more = battery in good condition
- 12.4-12.6V = battery partially discharged
- Below 12.4V = discharged, needs charging
- Below 12V = very discharged or faulty
Professional load test:
- Performed with a specialized tester applying a controlled load equal to 50% of the battery capacity and measuring its response for 15 seconds.
Optimal Preventive Maintenance
Monthly checks recommended
- Check the electrolyte level (for maintenance batteries)
- Clean terminal corrosion with baking soda
- Verify battery mounting in its tray
- Test the voltage with a digital multimeter
Proper usage practices
- Avoid complete discharges below 10.5V
- Do not leave loads on with the engine off for more than 30 minutes
- Drive the car regularly (at least 15-20 minutes weekly)
- Use a maintenance charger during long periods of inactivity
Proper storage
- Dry and cool location (5-25°C)
- Disconnect terminals for periods longer than 2 weeks
- Charge to 100% before long-term storage
- Recharge every 2-3 months if the vehicle is not used
Charging time for a car battery varies from minutes to several hours, depending on multiple factors. To maximize efficiency and battery life, opt for slow charging whenever possible, use quality equipment, and follow safety precautions.
The first sign that the battery is on the right track will come when you turn the key and the dashboard lights up normally. The better the battery is maintained and the more capable the charger used, the faster and more effectively you will charge a discharged car battery.