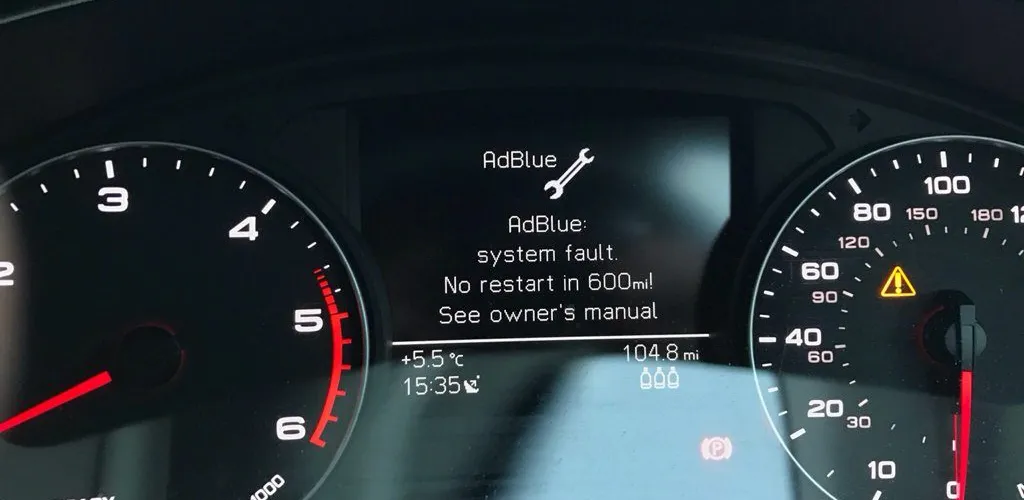
- AdBlue uses SCR to cut NOx, helping meet stricter diesel standards
- Repairs are costly: pumps, catalysts, and sensors often expensive to replace
- Removal requires ECU reprogramming to deactivate AdBlue functions
- If AdBlue fails, the vehicle may go into protective mode or not start
In recent years, the AdBlue system has become standard on most modern diesel cars, serving as an essential requirement to meet increasingly strict emission standards. While its role in reducing NOx emissions is undeniable, some vehicle owners face technical issues or repair costs that push them to consider removing this system.
In this article, we explore what uninstalling the AdBlue system entails, when it might be justified, and what consequences it carries.
What is the AdBlue system and how it works
AdBlue is an anti-pollution system introduced to reduce NOx emissions from diesel engines, enabling compliance with European environmental standards that are becoming ever stricter. The liquid used in this system has a simple composition: 32.5% urea and 67.5% deionized water.
The system operates using SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction). In the exhaust gas path from the combustion chamber, AdBlue is injected into the hot gas stream, where it reacts with nitrogen oxides (NOx) — the main pollutants in diesel exhaust. Through this chemical reaction, nitrogen oxides are transformed into nitrogen and water vapor, substances completely harmless to the environment.
The system includes several essential components: AdBlue reservoir (usually 10-25 liters), dosing pumps, injectors, level and temperature sensors, and the SCR catalyst. All of these are continuously monitored by the vehicle’s on-board computer.
Reasons why owners want to remove the AdBlue system
Expensive system failures
The main reason owners consider removing the AdBlue system is technical malfunctions and repair costs. A car with a faulty AdBlue system or an empty reservoir enters a protective mode: the engine may not start or power is severely limited, and the car becomes practically unusable.
Repair costs can be substantial. Replacing the dosing pump can cost between 2,000 and 4,000 RON, while a faulty SCR catalyst can reach 5,000-8,000 RON, depending on the model. Labor costs add to this and can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the intervention and the vehicle brand.
Faulty sensors, clogged pipes due to urea crystallization, or problems with the system control module are common faults, especially on older cars or those not properly maintained.
The operating costs myth
Some owners cite the extra cost of purchasing AdBlue as a reason to remove the system. However, this justification does not hold up under economic analysis. One liter of AdBlue costs about 5-7 RON and is enough for roughly 1,000 km of driving. At an average operating cost, this amounts to only 0.50-0.70 RON per 100 km, a negligible sum compared to other maintenance costs of a vehicle.
Technical process of uninstalling the AdBlue system
Electronic method
The AdBlue system can be removed only through electronic uninstall, a process that involves several complex technical operations:
ECU reprogramming: The engine software is modified to deactivate all AdBlue-related functions. Practically, the on-board computer is deceived into thinking the system is operating within optimum parameters.
Sensor deactivation: Level, temperature and fluid-quality sensors are electronically disabled, so they no longer send error signals to the control unit.
Disabling warnings: Fault warning indicators on the instrument cluster that would normally signal AdBlue issues are suppressed in software.
Circuit blocking: The software connection between the engine itself and the AdBlue injection system is interrupted, so a lack of fluid or faults no longer affect engine operation.
Duration and complexity of the intervention
Although some tuning service providers promote that uninstall can be done in about 30 minutes, the reality is more complex. The actual duration depends on the vehicle model, the generation of the AdBlue system, and the technician’s experience.
For some newer models, with advanced protection systems, the process can take several hours and require specialized programming equipment. It is essential that the operation is performed by a professional with experience in ECU reprogramming, not by any Driver without experience as sometimes claimed.
Consequences of removing the AdBlue system
Impact on performance and fuel consumption
Following the electronic uninstall, many vehicles record a slight improvement in fuel consumption, on the order of 3-7%, due to removing restrictions in the engine maps. In addition, engine power may increase slightly as the ECU no longer needs to dose power to balance with the exhaust aftertreatment system.
However, these benefits come at the direct cost to the environment, as emissions of nitrogen oxides increase substantially.
Legal and environmental aspects
It is essential to understand that removing the AdBlue system is illegal in Romania and throughout the European Union. Vehicles modified in this way no longer comply with homologation standards and may be taken out of circulation during a rigorous technical inspection or a police check.
Beyond legal aspects, there are also significant ethical implications. Nitrogen oxides are dangerous pollutants that contribute to photochemical smog, to acid rain, and have serious health effects, affecting the respiratory system. Removing the AdBlue system means contributing directly to increased pollution in urban areas where air quality is already compromised.
Impact on resale value
A car with the AdBlue system deactivated will have a reduced resale value. Informed buyers will avoid such vehicles due to legal implications, while those unaware may face problems during ITP or in other technical inspections.
Alternatives to complete removal of the system
Professional repairs
Before deciding to remove the system, it’s worth exploring repair options. Many faults can be remedied at reasonable costs:
- Cleaning the reservoir and clogged pipes: 300-800 RON
- Replacing faulty sensors: 200-600 RON
- Reprogramming the control module: 500-1,000 RON
Preventive maintenance
Proper maintenance can prevent many problems:
- Use only AdBlue of certified ISO 22241 quality
- Refill the reservoir before the level reaches minimum
- Avoid leaving the car with the reservoir near empty
- In cold seasons, ensure AdBlue does not freeze (freezes at -11°C)
- Carry out periodic checks of the system at authorized service centers
Conclusion: A decision that requires careful evaluation
While uninstalling the AdBlue system may seem an attractive solution in the face of costly faults, we must weigh all aspects carefully: legality, environmental impact, resale consequences, and potential fines or issues with authorities.
In the vast majority of cases, investing in professional repair or thorough preventive maintenance is wiser than removing the system. If repair costs are too high and the car is aging, it may be time to consider replacing the vehicle with a newer, more reliable one.
Whatever decision you make, it is important to be aware of all implications and to take responsibility for your choice — both toward your vehicle and toward the environment and society.